Leukemia is a form of can.cer marked by the abnormal production of white blood cells in the bone marrow. It affects countless people globally, particularly those with weakened immune systems, who are at an even higher risk of developing the disease.
Without timely and appropriate treatment, leukemia can lead to serious complications such as anemia, infections, and excessive bleeding.
The good news is that leukemia is often treatable, and many patients respond well to therapy, sometimes even achieving full recovery.
Early Detection: Recognizing the Signs
Identifying leukemia early significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. To that end, it’s important to pay attention to warning signs that may appear in the early stages. Below are 15 symptoms commonly associated with leukemia:
1. Persistent fatigue: A shortage of red blood cells can result in constant tiredness and a general lack of energy.
2. Loss of motivation: A feeling of discouragement or lack of drive may occur at the onset of the disease.
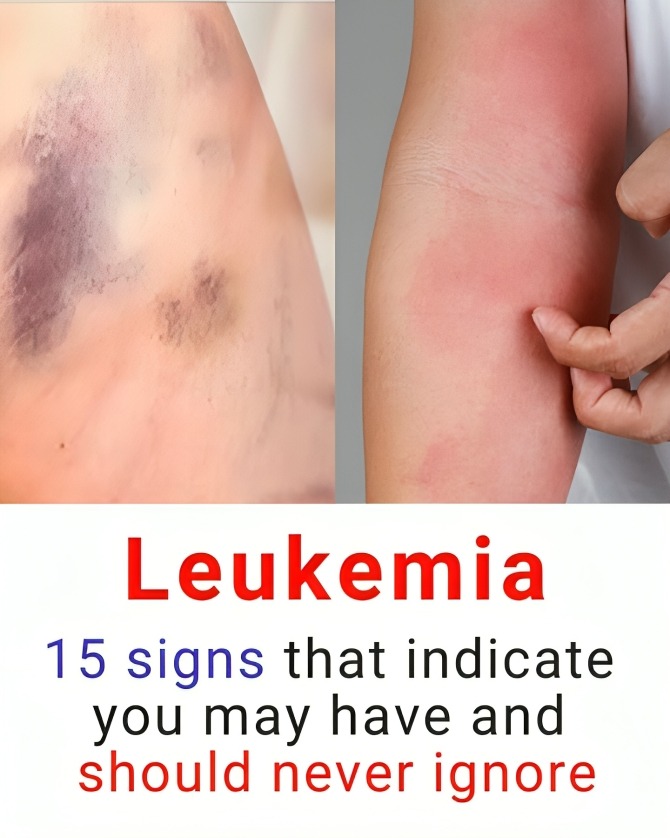
3. Unusual bleeding: Frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums can be an early indicator.
4. Unexplained bruising: Small red or purple spots on the skin with no clear cause could be a sign.
5. Swollen gums: Gum inflammation is often observed in leukemia cases.
6. Bloating and decreased appetite: An enlarged spleen may lead to abdominal discomfort and reduced hunger.

7. Pain in the upper left abdomen: Discomfort or pain in this area may signal spleen enlargement, which can worsen without medical attention.
8. Low-grade fever: A slight fever (around 37°C) can signal infection or immune system dysfunction and appears in roughly 25% of leukemia patients.
9. Excessive night sweats: Profuse sweating without physical exertion or heat exposure should be medically assessed.
10. Facial paralysis: Although rare, facial paralysis can be linked to leukemia or even a stroke, requiring urgent evaluation.
11. Pale skin and sleepiness: These are common symptoms of anemia, which may result from leukemia.
12. Bone discomfort: Pain in bones or joints can also be a symptom that warrants medical investigation.
13. Swollen lymph nodes: Enlarged glands in the neck, armpits, or groin may signal an infection related to leukemia.
14. Skin rashes: Skin changes or rashes can emerge and worsen as the disease progresses.
15. Frequent infections: Regular occurrences of mild infections may suggest a compromised immune system, a common effect of leukemia.
If you or someone you know is experiencing several of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate tests.
Important Reminder:
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. If you suspect any health issues or have concerns about symptoms, always consult a qualified medical provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Living with Leukemia: The Role of Mental Health, Lifestyle, and Support Systems
Being diagnosed with leukemia can be an overwhelming and life-changing experience. Beyond the physical symptoms and medical treatments, patients often face emotional, psychological, and social challenges that can greatly impact their quality of life. Understanding and addressing these factors is crucial in supporting overall well-being and improving treatment outcomes.
Mental health plays a vital role in how individuals cope with leukemia. It’s common for patients to experience anxiety, depression, fear, and uncertainty, especially after diagnosis or during intense treatment phases. Psychological support through therapy, counseling, or support groups can help patients process their emotions, build resilience, and maintain a positive outlook—factors that are known to aid recovery and enhance adherence to medical plans.
Lifestyle choices can also have a significant impact. While leukemia itself is not directly caused by diet or exercise, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support the immune system and reduce the risk of complications. A balanced diet rich in nutrients, regular light physical activity (as advised by a doctor), proper sleep, and hydration can all contribute to better physical and mental health. Avoiding smoking, alcohol, and exposure to environmental toxins is also recommended.
Social support is another cornerstone of recovery. Family, friends, and caregivers play a powerful role in helping patients feel supported and not alone in their journey. Even small gestures—like accompanying someone to a doctor’s appointment or preparing a healthy meal—can make a significant difference. Community and online support groups also offer opportunities for sharing experiences, reducing isolation, and gaining practical advice.
Education and self-advocacy empower patients to participate in their care. Understanding their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential side effects helps individuals make informed decisions. Healthcare providers should always encourage open communication, where patients feel heard and respected.